- THE MONNALISA TOUCH
- ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY
- VERIFICATION OF INFERTILITY
- NEXPLANON
- ONCOLOGICAL SCREENING
- PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS
- DIAGNOSTIC ULTRASOUND
- FUNCTIONAL COSMETIC GYNECOLOGICAL SURGERY
- TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE (SUI)
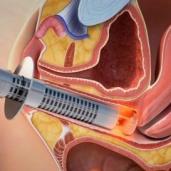
ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY
OFFICE HYSTEROSCOPY
OFFICE HYSTEROSCOPY
FURTHER READING TOPIC
For further reading on the subject, evaluation of cases, vision of events or consultation of scientific articles, please refer to the specific sections COMMUNICATIONS, COURSES AND CONFERENCES, SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTION and EVENT.
For further reading on the subject, evaluation of cases, vision of events or consultation of scientific articles, please refer to the specific sections COMMUNICATIONS, COURSES AND CONFERENCES, SCIENTIFIC PRODUCTION and EVENT.

News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. ISABELLA CHAPIESKI
From 04 to 22 November 2024 Dr. Isabella Chapieski from the city of San Paolo read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. ISABELLA CHAPIESKI
From 04 to 22 November 2024 Dr. Isabella Chapieski from the city of San Paolo read more
News
DATA OF THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL TRAINING ON LASER TECHNOLOGY IN SAN MARINO
For over 32 years CO2 laser activity has always been a high-tech treatment that read more
DATA OF THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL TRAINING ON LASER TECHNOLOGY IN SAN MARINO
For over 32 years CO2 laser activity has always been a high-tech treatment that read more
News
2025.10.25 GYN LAB SURGICAL
On 25.10.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of theoretical-practical training a read more
2025.10.25 GYN LAB SURGICAL
On 25.10.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of theoretical-practical training a read more
News
22.10.2024 TRAINING AND UPDATE DAY FOR PORTUGUESE DOCTORS
On 22.10.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of training and updating on new met read more
22.10.2024 TRAINING AND UPDATE DAY FOR PORTUGUESE DOCTORS
On 22.10.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of training and updating on new met read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. ANA VICTORIA VITRO DE CAMPOS
In the days from 02 to 21 October 2024 Dr. Ana Vetrória Vitro de Campos read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. ANA VICTORIA VITRO DE CAMPOS
In the days from 02 to 21 October 2024 Dr. Ana Vetrória Vitro de Campos read more
News
MYOSTATIN CHANGES IN FEMALES WITH UI AFTER MAGNETIC STIMULATION. A QUASI–EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
A multicenter quasi-experimental study published in the Journal Medicine aimed t read more
MYOSTATIN CHANGES IN FEMALES WITH UI AFTER MAGNETIC STIMULATION. A QUASI–EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
A multicenter quasi-experimental study published in the Journal Medicine aimed t read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. FERNANDA DE ARAUJO SOARES
In the days from 18 June to 28 June 2024 Dr. Fernanda de Araujo Soares coming read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF DR. FERNANDA DE ARAUJO SOARES
In the days from 18 June to 28 June 2024 Dr. Fernanda de Araujo Soares coming read more
News
THE EFFICACY OF CO2 VAGINAL LASER IN THE TREATMENT OF RECURRENT, POST–COITAL AND INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS: A MULTICENTRIC PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Multicenter prospective study published in the Journal Clinical Medicine condu read more
THE EFFICACY OF CO2 VAGINAL LASER IN THE TREATMENT OF RECURRENT, POST–COITAL AND INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS: A MULTICENTRIC PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Multicenter prospective study published in the Journal Clinical Medicine condu read more
News
06.06.2024 TRAINING AND UPDATE DAY FOR BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 06.00.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of training and updating on new met read more
06.06.2024 TRAINING AND UPDATE DAY FOR BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 06.00.2024 Dr. Filippini conducted a day of training and updating on new met read more
News
WCAG World Congress in Cartagena de Indias (Colombia)
13-15.03.2024 Speeches by Dr. Filippini at the WCAG World Congress in Cartagena read more
WCAG World Congress in Cartagena de Indias (Colombia)
13-15.03.2024 Speeches by Dr. Filippini at the WCAG World Congress in Cartagena read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM AUSTRIA
On 27-28 February 2024 a group of doctors from Austria carried out a training i read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM AUSTRIA
On 27-28 February 2024 a group of doctors from Austria carried out a training i read more
News
THE UTILITY OF CO2 LASER TREATMENT OF PELVIC SYMPTOMS IN WOMEN WITH PREVIOUS PERINEAL TRAUMA DURING DELIVERY
Article published in the MDPI Journal of Personalized Medicine which evaluates t read more
THE UTILITY OF CO2 LASER TREATMENT OF PELVIC SYMPTOMS IN WOMEN WITH PREVIOUS PERINEAL TRAUMA DURING DELIVERY
Article published in the MDPI Journal of Personalized Medicine which evaluates t read more
News
09.11.2023 THEORETICAL PRACTICAL COURSE ON CO2 LASER HELD IN MILAN
Theoretical-practical course on CO2 laser and electromagnetic chair for a limite read more
09.11.2023 THEORETICAL PRACTICAL COURSE ON CO2 LASER HELD IN MILAN
Theoretical-practical course on CO2 laser and electromagnetic chair for a limite read more
News
2023.11.02 REPORT FROM THE DEKA ACADEMY TO BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 2023.11.02 Dr. Filippini held a course on the new laser and electromagnetic t read more
2023.11.02 REPORT FROM THE DEKA ACADEMY TO BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 2023.11.02 Dr. Filippini held a course on the new laser and electromagnetic t read more
News
28.10.2023 INTERNATIONAL WEBINAR ON ENERGIES IN GYNECOLOGY BY SBLMC
10.28.2023 Report by Dr. Filippini International Webinar on Energies in Enology read more
28.10.2023 INTERNATIONAL WEBINAR ON ENERGIES IN GYNECOLOGY BY SBLMC
10.28.2023 Report by Dr. Filippini International Webinar on Energies in Enology read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM GERMANY AND AUSTRIA
On October 25 2023 a group of doctors from Germany and Austria carried out a t read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM GERMANY AND AUSTRIA
On October 25 2023 a group of doctors from Germany and Austria carried out a t read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM PORTUGAL
On June 20-21 2023 a group of Doctors from Latvia conducted a training interns read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM PORTUGAL
On June 20-21 2023 a group of Doctors from Latvia conducted a training interns read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF TWO GREAT BRAZILIAN FRIENDS
On 26-28 June 2023 two great friends from Brazil undertook a training course at read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF TWO GREAT BRAZILIAN FRIENDS
On 26-28 June 2023 two great friends from Brazil undertook a training course at read more
News
THE EFFICACY AND FEASIBILITY OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE: A MULTICENTRIC CASE–CONTROL STUDY
Article by the LARA group on 'Efficacy and feasibility of fractional co2 las read more
THE EFFICACY AND FEASIBILITY OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER THERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE: A MULTICENTRIC CASE–CONTROL STUDY
Article by the LARA group on 'Efficacy and feasibility of fractional co2 las read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM LATVIA
On June 20-21 2023 a group of Doctors from Latvia conducted a training interns read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM LATVIA
On June 20-21 2023 a group of Doctors from Latvia conducted a training interns read more
News
2023.05.29 SPECIALIZATION THESIS ON 10 YEARS OF MONNALISA TOUCH LASER TREATMENTS IN THE REPUBLIC OF SAN MARINO
On Monday 29 May 2023 in the lecture hall of the Secretariat of the University read more
2023.05.29 SPECIALIZATION THESIS ON 10 YEARS OF MONNALISA TOUCH LASER TREATMENTS IN THE REPUBLIC OF SAN MARINO
On Monday 29 May 2023 in the lecture hall of the Secretariat of the University read more
News
A QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF MAGNETIC STIMULATION IN WOMEN WITH URINARY INCONTINENCE SYMPTOMS AND PELVIC FLOOR DISORDERS
Article published in the MDPI Medicine journal evaluating the efficacy and safet read more
A QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF MAGNETIC STIMULATION IN WOMEN WITH URINARY INCONTINENCE SYMPTOMS AND PELVIC FLOOR DISORDERS
Article published in the MDPI Medicine journal evaluating the efficacy and safet read more
News
2023.04.13 REPORT FROM THE DEKA ACADEMY TO BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 04.13.2023 Dr. Filippini held a course on the new laser and electromagnetic t read more
2023.04.13 REPORT FROM THE DEKA ACADEMY TO BRAZILIAN DOCTORS
On 04.13.2023 Dr. Filippini held a course on the new laser and electromagnetic t read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM SLOVENIA AND CROATIA
From 21 to 21 March 2023 a group of Doctors from Slovenia and Croatia carried o read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM SLOVENIA AND CROATIA
From 21 to 21 March 2023 a group of Doctors from Slovenia and Croatia carried o read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM PORTUGAL
In the days from 06 to 07 December 2022 a group of Doctors from Portugal carrie read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM PORTUGAL
In the days from 06 to 07 December 2022 a group of Doctors from Portugal carrie read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM TURKEY
From 29 to 30 November 2022 a group of Doctors from Turkey carried out a traini read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP OF A GROUP OF DOCTORS FROM TURKEY
From 29 to 30 November 2022 a group of Doctors from Turkey carried out a traini read more
News
TRAINING INTERNSHIP DR.SSA CARMEN LETICIA BARBOSA DE AZEVEDO
From 10 to 14 October 2022 Dr. Carmen Barbosa De Azevedo carried out a training read more
TRAINING INTERNSHIP DR.SSA CARMEN LETICIA BARBOSA DE AZEVEDO
From 10 to 14 October 2022 Dr. Carmen Barbosa De Azevedo carried out a training read more
News
ANTI–MULLERIAN HORMONE (AMH) AND ADENOMYOSIS: MINI–REVIEW OF LITERATURE OF THE LAST 5 YEARS
Article published in the journal Frontiers in Endocrinology to evaluate the corr read more
ANTI–MULLERIAN HORMONE (AMH) AND ADENOMYOSIS: MINI–REVIEW OF LITERATURE OF THE LAST 5 YEARS
Article published in the journal Frontiers in Endocrinology to evaluate the corr read more
News
2022.08.03 VISIT OF A FRIEND: THE MEXICAN ANTONIO POSADA
2022.08.03 Visit to our ward of our Mexican colleague Antonio Posada Jefe de Un read more
2022.08.03 VISIT OF A FRIEND: THE MEXICAN ANTONIO POSADA
2022.08.03 Visit to our ward of our Mexican colleague Antonio Posada Jefe de Un read more
News
PRESS REVIEW ABOUT THE NEW ELECTROMAGNETIC DEVICE DR. ARNOLD
Press review of the San Marino newspapers on the occasion of the donation by th read more
PRESS REVIEW ABOUT THE NEW ELECTROMAGNETIC DEVICE DR. ARNOLD
Press review of the San Marino newspapers on the occasion of the donation by th read more
News
RESULT OF A FIVE–YEAR EXPERIENCE IN FIRST TRIMESTER PREECLAMPSIA
Article published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine about a monocentric study read more
RESULT OF A FIVE–YEAR EXPERIENCE IN FIRST TRIMESTER PREECLAMPSIA
Article published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine about a monocentric study read more
News
2022.05.31 VISIT OF A FRIEND: THE COLOMBIAN PABLO GONZALEZ ISAZA
Visit of Colombian friend Pablo Gonzalez Isaza specialist in Minimally Invasive read more
2022.05.31 VISIT OF A FRIEND: THE COLOMBIAN PABLO GONZALEZ ISAZA
Visit of Colombian friend Pablo Gonzalez Isaza specialist in Minimally Invasive read more
News
29–30.04.2022 THEORETICAL PRACTICAL COURSE ON CO2 LASER HELD IN PERUGIA
Theoretical-practical course on limited number of CO2 lasers held in Perugia at read more
29–30.04.2022 THEORETICAL PRACTICAL COURSE ON CO2 LASER HELD IN PERUGIA
Theoretical-practical course on limited number of CO2 lasers held in Perugia at read more
News
INTERVIEW ABOUT THE NEW DUOGLIDE LASER SYSTEM
Press article published in the newspaper L'INFORMAZIONE DI SAN MARINO on the read more
INTERVIEW ABOUT THE NEW DUOGLIDE LASER SYSTEM
Press article published in the newspaper L'INFORMAZIONE DI SAN MARINO on the read more
News
CO2–LASER THERAPY AND GENITOURINARY SYNDROME OF MENOPAUSE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META–ANALYSIS
Article by Dr. Maurizio Filippini published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine in read more
CO2–LASER THERAPY AND GENITOURINARY SYNDROME OF MENOPAUSE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META–ANALYSIS
Article by Dr. Maurizio Filippini published in The Journal of Sexual Medicine in read more
News
EFFECTS OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER TREATMENT ON PATIENTS AFFECTED BY VULVAR LICHEN SCLEROSUS: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Article by Dott. Maurizio Filippini published in the journal Photomedicine and L read more
EFFECTS OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER TREATMENT ON PATIENTS AFFECTED BY VULVAR LICHEN SCLEROSUS: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
Article by Dott. Maurizio Filippini published in the journal Photomedicine and L read more
News
SATISFACTION WITH PROPHYLACTIC RISK–REDUCING SALPINGO–OOPHORECTOMY IN BRCA MUTATION CARRIERS
Article by Dr. Margaret Sammarini published in Menopause The Journal of The Nor read more
SATISFACTION WITH PROPHYLACTIC RISK–REDUCING SALPINGO–OOPHORECTOMY IN BRCA MUTATION CARRIERS
Article by Dr. Margaret Sammarini published in Menopause The Journal of The Nor read more
News
THE BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER TREATMENT ON PERINEAL CHANGES DURING PUERPERIUM
Multicenter retrospective study (State Hospital of the Republic of San Marino C read more
THE BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF FRACTIONAL CO2 LASER TREATMENT ON PERINEAL CHANGES DURING PUERPERIUM
Multicenter retrospective study (State Hospital of the Republic of San Marino C read more
News
VIDEO ILLUSTRATING THE EFFICIENCY OF LASER MONNALISA TOUCH TREATMENT IN VARIOUS GENITAL PATHOLOGIES
In the "VIDEO" section there are some videos illustrating the advantag read more
VIDEO ILLUSTRATING THE EFFICIENCY OF LASER MONNALISA TOUCH TREATMENT IN VARIOUS GENITAL PATHOLOGIES
In the "VIDEO" section there are some videos illustrating the advantag read more
News
CURRENT INDICATIONS FOR LASER TREATMENT ACCORDING TO THE SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCES PRESENT IN LITERATURE
The main indications about the use of the MonnaLisa Touch laser treatment on som read more
CURRENT INDICATIONS FOR LASER TREATMENT ACCORDING TO THE SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCES PRESENT IN LITERATURE
The main indications about the use of the MonnaLisa Touch laser treatment on som read more
News
MONNALISA TOUCH: MORE THAN 3100 TREATMENTS
The authorized center of the Republic of San Marino was among the first centers read more
MONNALISA TOUCH: MORE THAN 3100 TREATMENTS
The authorized center of the Republic of San Marino was among the first centers read more
News
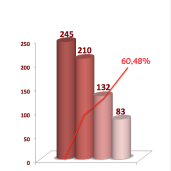
MONNALISA TOUCH THE LASER TREATMENT RESULTS OF 2018/09/30
Look at the statistics of MonnaLisa Touch treatment performed in the vagina̴ read more
MONNALISA TOUCH THE LASER TREATMENT RESULTS OF 2018/09/30
Look at the statistics of MonnaLisa Touch treatment performed in the vagina̴ read more
News
BEFORE THE MASTER THESIS MONNALISA TOUCH
Wednesday January 21 2015 to complete the Masters in Aesthetic Surgery of the read more
BEFORE THE MASTER THESIS MONNALISA TOUCH
Wednesday January 21 2015 to complete the Masters in Aesthetic Surgery of the read more
News
FIRST THESIS ON MONNALISA TOUCH
Tuesday July 22 2014 in the classroom of the Secretariat of the University of read more
FIRST THESIS ON MONNALISA TOUCH
Tuesday July 22 2014 in the classroom of the Secretariat of the University of read more
News
AUTHORIZED TREATMENT CENTER TOUCH MONNALISA
Since the beginning of 2013 the State Hospital of the Republic of San Marino ha read more
AUTHORIZED TREATMENT CENTER TOUCH MONNALISA
Since the beginning of 2013 the State Hospital of the Republic of San Marino ha read more
News
COURSES OF LASER TECHNOLOGY
Intensive theoretical and practical courses individuals or small groups on the read more
COURSES OF LASER TECHNOLOGY
Intensive theoretical and practical courses individuals or small groups on the read more
NEWSLETTER
Sign up for our newsletter to keep informed about our offers
Sign up for our newsletter to keep informed about our offers
Enquiry
WHAT GUESTS SAY ABOUT US